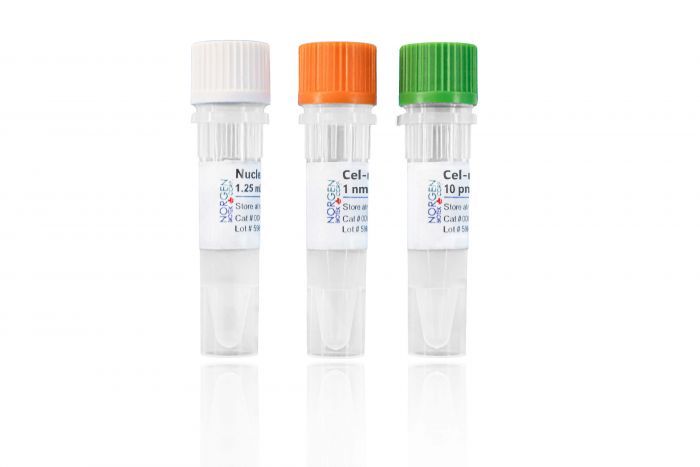
microRNA (cel-miR-39) Spike-In Kit
A quantified synthetic RNA (cel-miR-39) for spike-in during RNA extraction procedures and subsequent normalization in RT-qPCR assays

For research use only and NOT intended for in vitro diagnostics.
microRNA (cel-miR-39) Spike-In Kit
A quantified synthetic RNA (cel-miR-39) for spike-in during RNA extraction procedures and subsequent normalization in RT-qPCR assays
Register today to receive an exclusive 15% off* on your first order.
Features and Benefits
- Well-accepted microRNA sequence used for normalization in gene expression studies
- Best suited for RNA purification from samples with low RNA abundance including liquid biopsies (plasma/serum/urine etc.) and low cell or tissue inputs
- Compatible to expression analysis using RT-qPCR - both RNA and matching forward PCR primer provided.
- Fully compatible to Norgen's microScript cDNA Synthesis system
- Fully compatible to Next Generation Sequencing (Small RNA-Seq) library preparation workflow
The amount of RNA that can be extracted from different biological or clinical samples varies greatly. For example, while a few micrograms of RNA could be easily purified from tissues and cells in excess amounts (such as from a few milligrams of tissue), many liquid biopsy samples may yield very low amounts of RNA. In fact, samples such as urine or plasma may yield 1 - 100 ng or less RNA per 100 µL of sample. Such a range of RNA quantity is often below the detection limit of most commonly used techniques for measuring RNA including nano-spectrophotometry and fluorescent nucleic acid stains. As a result, without properly determined RNA concentration, it becomes very difficult to normalize the starting quantity of RNA used in gene expression studies.
Norgen’s microRNA (cel-miR-39) Spike-In Kit offers a quantified synthetic RNA (cel-miR-39) for spike-in during RNA extraction procedures and subsequent normalization in RT-qPCR assays. The amount of cel-miR-39 RNA recovered after RNA extraction is directly correlated with the amount of total RNA recovered. After reverse transcription (such as with Norgen’s microScript Reverse Transcription system) of the sample RNA (with spike-in), the level of cel-miR-39 can be determined by subjecting the cDNA generated to quantitative PCR (qPCR) using fluorescent nucleic acid stains such as SYBR Green. A cel-miR-39 specific primer is included in the kit. The level of expression of any target transcripts in different RNA samples can now be normalized to the cel-miR-39 transcript level using standard method such as ∆∆Ct relative quantification.
In addition, the cel-miR-39 RNA is compatible to library preparation methods (including ligation-based protocols) in Next Generation Sequencing (Small RNA-Seq) workflows. The cel-miR-39 RNA could be used for normalization as well as for tracking library construction efficiency.
Details
Supporting Data
Figure 1. Accurate Quantity and High Quality cel-miR-39 Spike-In. Various quantities of the reconstituted cel-miR-39 RNA was used as spike-in during isolation of urinary RNA (1 mL) using Norgen's Urine Exosome RNA Isolation Kit (Cat. 47200). Isolated RNA was reverse transcribed using Norgen's microScript cDNA Synthesis Kit (Cat. 54410), followed by qPCR using Norgen's 2X PCR Master Mix (Cat. 28007), supplemented with SYBR Green I. The cel-miR-39 RNA was successfully detected in all samples, with the Ct values distributed according to the amount of RNA spiked-in.
Figure 2. Successful Incorporation of cel-miR-39 Spike-In into Small RNA-Seq Library. Small RNA-Seq Library was generated using either a competitor’s or Norgen's cel-miR-39 Spike-In RNA at two concentrations (High and Low). The library was generated using Illumina's TruSeq Small RNA Library Preparation Kit. The incorporated libraries were resolved on a PAGE gel. Only Norgen's cel-miR-39 RNA showed effective incorporation into small RNA-Seq library (Red Arrows). The competitor's cel-miR-39 RNA only yielded bands (Yellow Arrows) equivalent to the No Template Control (NTC) that are adapter dimers.
Storage Conditions
Upon receipt, store Norgen’s microRNA (cel-miR-39) Spike-In Kit at -20°C or lower. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. If needed, prepare smaller working aliquots and store at -20°C or lower.
Component | Cat. 59000 |
|---|---|
cel-miR-39 RNA | 10 pmol |
cel-miR-39 Forward PCR Primer | 1 nmol |
Nuclease-Free Water | 1.25 mL |
Product Insert | 1 |
Documentation
Citations
| Title | Candidate circulating microRNA biomarkers in dogs with chronic pancreatitis |
| Citation | Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine 2024. |
| Authors | Susan K. Armstrong 1 | Robert W. Hunter2 | Wilna Oosthyuzen3 | Maciej Parys 3 | Adam G. Gow4 | Silke Salavati Schmitz3 | James W. Dear5 | Richard J. Mellanby3 |
| Title | m6A modification inhibits miRNAs' intracellular function, favoring their extracellular export for intercellular communication |
| Citation | Cell reports medicine 2024. |
| Authors | Sabrina Garbo Daniel D'Andrea Alessio Colantoni Francesco Fiorentino Antonello Mai Andres Ramos Gian Gaetano Tartaglia Andrea Tancredi Marco Tripodi 9 Cecilia Battistelli |
| Title | miR-541 is associated with the prognosis of liver cirrhosis and directly targets JAG2 to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells |
| Citation | BMC Gastroenterology 2024. |
| Authors | Jin-Pei Liu, Shao-Hua Song, Pei-Mei Shi, Xiao-Yu Qin, Bai-Nan Zheng, Shu-Qing Liu, Chen-Hong Ding, Xin Zhang, Wei-Fen Xie, Yi-Hai Shi & Wen-Ping Xu |
| Title | Plasma Circulating Terminal Differentiation- Induced Non-Coding RNA Serves as a Biomarker in Breast Cancer |
| Citation | IJHOSCR 2024. |
| Authors | Zeynab Shaghaghi Torkdari, Mohammad Khalaj-Kondori, Mohammad Ali Hosseinpour Feizi |
| Title | tRNAGlu-derived fragments from embryonic extracellular vesicles modulate bovine embryo hatching |
| Citation | Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology 2024. |
| Authors | Yuan Fan, Krishna Chaitanya Pavani, Katrien Smits, Ann Van Soom & Luc Peelman |
| Title | Use of Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction to Identify Biomarkers for Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Renal Masses |
| Citation | Cancers 2024. |
| Authors | Joshua P. Hayden 1,Adam Wiggins 1,Travis Sullivan 2,Thomas Kalantzakos 2,Kailey Hooper 2,Alireza Moinzadeh 1 andKimberly Rieger-Christ 1,2,* |
| Title | Effects of Cow's Milk Processing on MicroRNA Levels |
| Citation | foods 2023. |
| Authors | Loubna Abou el qassim, Beatriz Martínez, Ana Rodríguez, Alberto Dávalos, María-Carmen López de las Hazas, Mario Menéndez Miranda and Luis J. Royo |
| Title | Gene Expression Analysis of nc-RNAs in Bipolar and Panic Disorders: A Pilot Study |
| Citation | Genes 2023. |
| Authors | Fabrizio Bella, Maria Rosaria Anna Muscatello, Angela D'Ascola and Salvatore Campo |
| Title | Impact of storage conditions and duration on function of native and cargo-loaded mesenchymal stromal cell extracellular vesicles |
| Citation | Cytotherapy 2023. |
| Authors | Daniel Levy , Anjana Jeyaram , Louis J. Born , Kai-Hua Chang , Sanaz Nourmohammadi Abadchi , Angela Ting Wei Hsu , Talia Solomon , Amaya Aranda , Samantha Stewart , Xiaoming He , John W. Harmon , Steven M. Jay |
| Title | Role of d-tocotrienol and resveratrol supplementation in the regulation of micro RNAs in patients with metabolic syndrome: A randomized controlled trial |
| Citation | Complementary Therapies in Medicine 2023. |
| Authors | Safia Fatima, Dilshad Ahmed Khan, Fozia Fatima, Muhammad Aamir, Aamir Ijaz, Ayesha Hafeez, |