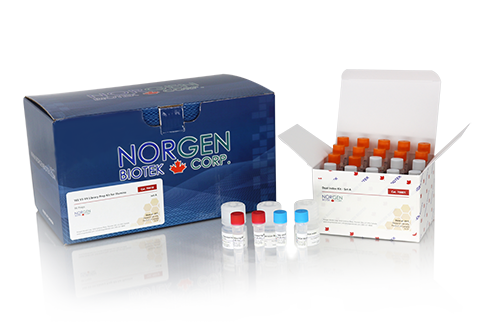
- Simple and quick workflow. Library could be prepared in less than 4 hours
- Part of Norgen’s metagenomics workflow: collection, preservation, DNA isolation, sequencing, and analysis
- Protocol optimized for DNA isolated from a large range of sample types
- Up to 384 unique dual-index libraries can be prepared for a single NGS run
Filter:

The reagents and components required for library preparation of the 16S V4 amplicon libraries to be used for next-generation sequencing on Illumina platforms

The reagents and components required for library preparation of the 16S V4-V5 amplicon libraries to be used for next-generation sequencing on Illumina platforms

The reagents and components required for library preparation of the 16S V4-V5 amplicon libraries to be used for next-generation sequencing on Illumina platforms

The reagents and components required for library preparation of the 16S V4-V5 amplicon libraries to be used for next-generation sequencing on Illumina platforms

The reagents and components required for library preparation of the 16S V4-V5 amplicon libraries to be used for next-generation sequencing on Illumina platforms

The reagents and components required for library preparation of the 16S V4 amplicon libraries to be used for next-generation sequencing on Illumina platforms

The reagents and components required for library preparation of the 16S V4 amplicon libraries to be used for next-generation sequencing on Illumina platforms

The reagents and components required for library preparation of the 16S V3-V5 amplicon libraries to be used for next-generation sequencing on Illumina platforms

The reagents and components required for library preparation of the 16S V3-V5 amplicon libraries to be used for next-generation sequencing on Illumina platforms

The reagents and components required for library preparation of the 16S V4-V5 amplicon libraries to be used for next-generation sequencing on Illumina platforms

The reagents and components required for library preparation of the 16S V4 amplicon libraries to be used for next-generation sequencing on Illumina platforms

The reagents and components required for library preparation of the 16S V4 amplicon libraries to be used for next-generation sequencing on Illumina platforms
Prepare Consistent High Quality 16S rRNA Libraries with Streamlined Workflow
The 16S ribosomal RNA gene (16S rRNA) is a common target for microbial community classification in metagenomic studies. The gene is approximately 1,500 bp long and contains nine variable regions interspersed between conserved regions. These variable regions are frequently used in phylogenetic classifications such as genus or species in diverse microbial populations. The 16S region to sequence is an area of debate, and your region of interest might vary depending on multiple factors including experimental objectives, design, and sample type.
Norgen offers optimized 16S sequencing library preparation kits that accommodate a range of sample types and input quantities. Our library prep kits provide end-users with a streamlined workflow experience that consistently yield high-quality NGS libraries across a range of sample types. With Norgen offering NGS library preparation kits for nine 16S regions, and multiplex panels of both 16S, you can choose the kit that best suits your research needs. Our library preparation kits come in sizes to accommodate as few as 24 samples and as many as 384 uniquely-indexed samples that can be sequenced in a single NGS run.
16S rRNA Library Preparation
Find the right kit for your sample type.
Norgen's optimized 16S sequencing library preparation kits accommodate a wide range of sample types and input quantities.
Using the Interactive Variable Region Diagram, select any of the regions below to learn which of Norgen's 16S rRNA Library Prep Kits is right for you and which regions are best for identifying specific microbial species.
Region V1 to V2 (Nucleotides 69-242)
- Used to distinguish Streptococcus sp. and differentiate between Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase negative Staphylococcus species
- Able to distinguish among Staphylococcal, Streptococcal, Clostridium, Haemophilus and Neisseria species
- Best target for distinguishing among Mycobacterium sp.
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteriodaceae, Clostridiaceae, Deinococcaceae, Enterococcaceae, Helicobacteraceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Neisseriaceae, Propionibacteriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at the Family level only
- Not useful for most Escherichia sp., Shigella sp., K. pneumoniae and E. aerogene
Region V1 to V3 (Nucleotides 69-497)
- Used to distinguish Staphylococci populations
- Able to detect Prevotella, Porphyromonas, and Bacteroides
Region V1 to V2 (Nucleotides 69-242)
- Used to distinguish Streptococcus sp. and differentiate between Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase negative Staphylococcus species
- Able to distinguish among Staphylococcal, Streptococcal, Clostridium, Haemophilus and Neisseria species
- Best target for distinguishing among Mycobacterium sp.
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteriodaceae, Clostridiaceae, Deinococcaceae, Enterococcaceae, Helicobacteraceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Neisseriaceae, Propionibacteriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at the Family level only
- Not useful for most Escherichia sp., Shigella sp., K. pneumoniae and E. aerogene
Region V1 to V3 (Nucleotides 69-497)
- Used to distinguish Staphylococci populations
- Able to detect Prevotella, Porphyromonas, and Bacteroides
Region V1 to V2 (Nucleotides 69-242)
- Used to distinguish Streptococcus sp. and differentiate between Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase negative Staphylococcus species
- Able to distinguish among Staphylococcal, Streptococcal, Clostridium, Haemophilus and Neisseria species
- Best target for distinguishing among Mycobacterium sp.
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteriodaceae, Clostridiaceae, Deinococcaceae, Enterococcaceae, Helicobacteraceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Neisseriaceae, Propionibacteriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at the Family level only
- Not useful for most Escherichia sp., Shigella sp., K. pneumoniae and E. aerogene
Region V2 to V3 (Nucleotides 137-497)
- Targets speciation among Staphylococcal and Streptococcal pathogens as well as Clostridium and Niesseria, Mycobacterium, and Haemophilius
Region V1 to V3 (Nucleotides 69-497)
- Used to distinguish Staphylococci populations
- Able to detect Prevotella, Porphyromonas, and Bacteroides
Region V2 to V3 (Nucleotides 137-497)
- Targets speciation among Staphylococcal and Streptococcal pathogens as well as Clostridium and Niesseria, Mycobacterium, and Haemophilius
Region V1 to V3 (Nucleotides 69-497)
- Used to distinguish Staphylococci populations
- Able to detect Prevotella, Porphyromonas, and Bacteroides
Region V2 to V3 (Nucleotides 137-497)
- Targets speciation among Staphylococcal and Streptococcal pathogens as well as Clostridium and Niesseria, Mycobacterium, and Haemophilius
Region V3 to V4 (Nucleotides 433-682)
- Better than region V2 in distinguishing between enterobacteriaceae K. pneumoniae and E. aerogenes
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteroidaceae, Clostridiaceae, Enterococcaceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Neisseriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at the Family level only
Region V1 to V3 (Nucleotides 69-497)
- Used to distinguish Staphylococci populations
- Able to detect Prevotella, Porphyromonas, and Bacteroides
Region V3 to V5 (Nucleotides 433-879)
- Able to detect Coxiellaceae, Enterococcaceae, and unclassified families within Firmicutes amd Tenericutes
Region V3 to V4 (Nucleotides 433-682)
- Better than region V2 in distinguishing between enterobacteriaceae K. pneumoniae and E. aerogenes
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteroidaceae, Clostridiaceae, Enterococcaceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Neisseriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at the Family level only
Region V3 to V5 (Nucleotides 433-879)
- Able to detect Coxiellaceae, Enterococcaceae, and unclassified families within Firmicutes amd Tenericutes
Region V4 (Nucleotides 576-682)
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteriodaceae, Clostridiaceae, Deinococcaceae, Enterococcaceae, Helicobacteraceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Propionibacteriaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae, Neisseriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae at the Family level only
Region V3 to V4 (Nucleotides 433-682)
- Better than region V2 in distinguishing between enterobacteriaceae K. pneumoniae and E. aerogenes
- Able to detect Actinomycetaceae, Bacillaceae, Bacteroidaceae, Clostridiaceae, Enterococcaceae, Lactobacillaceae, Listeriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Neisseriaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, Staphylococcaceae, Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at the Family level only
Region V4 to V5 (Nucleotides 576-879)
- Able to detect P. acnes and B. cepacia
Region V3 to V5 (Nucleotides 433-879)
- Able to detect Coxiellaceae, Enterococcaceae, and unclassified families within Firmicutes amd Tenericutes
Region V4 to V5 (Nucleotides 576-879)
- Able to detect P. acnes and B. cepacia
Region V3 to V5 (Nucleotides 433-879)
- Able to detect Coxiellaceae, Enterococcaceae, and unclassified families within Firmicutes amd Tenericutes
Region V4 to V5 (Nucleotides 576-879)
- Able to detect P. acnes and B. cepacia
Region V3 to V5 (Nucleotides 433-879)
- Able to detect Coxiellaceae, Enterococcaceae, and unclassified families within Firmicutes amd Tenericutes
Region V5 to V7 (Nucleotides 822-1173)
- Able to detect Cyanobacteria and picocyanobacterial communities, such as Synechococcus, Prochlorococcus, and Cyanobium
Region V5 to V7 (Nucleotides 822-1173)
- Able to detect Cyanobacteria and picocyanobacterial communities, such as Synechococcus, Prochlorococcus, and Cyanobium
Region V5 to V7 (Nucleotides 822-1173)
- Able to detect Cyanobacteria and picocyanobacterial communities, such as Synechococcus, Prochlorococcus, and Cyanobium
Region V5 to V7 (Nucleotides 822-1173)
- Able to detect Cyanobacteria and picocyanobacterial communities, such as Synechococcus, Prochlorococcus, and Cyanobium
Region V5 to V7 (Nucleotides 822-1173)
- Able to detect Cyanobacteria and picocyanobacterial communities, such as Synechococcus, Prochlorococcus, and Cyanobium
Region V7 to V9 (Nucleotides 1117-1465)
- Able to detect Veillonella populations
- Able to detect Deinococcaceae, Moraxellaceae, and Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at Family level only
Region V7 to V9 (Nucleotides 1117-1465)
- Able to detect Veillonella populations
- Able to detect Deinococcaceae, Moraxellaceae, and Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at Family level only
Region V7 to V9 (Nucleotides 1117-1465)
- Able to detect Veillonella populations
- Able to detect Deinococcaceae, Moraxellaceae, and Streptococcaceae at both the Family and Genus level
- Able to detect Enterobacteriaceae at Family level only