Understanding Metabolomics
In recent times, microbiome studies have rapidly increased in popularity, ranging in application from cancer to weight loss. While many human gut microbiome studies focus on genetic barcoding to identify which species are present in a given stool sample, much can also be learned by the metabolites that are present. Metabolites are the byproduct of the metabolic process, which is how the human body creates the energy and compounds it needs to function by breaking down food, chemicals, drugs and/or tissue. By looking at the end product, it is possible to analyze the interactions between an organism and its microflora, or just between the microflora themselves, whether within a host or simply in the environment. The study of these metabolites, which is referred to as metabolomics, can be used to understand the biochemical activity of cells and provide insight into their physiology.
The most common type of sample for a metabolomic study is-and no prizes here if you guessed it-a stool sample. Now, we all know the wide variety of forms that this sample type can take, so having a "one size fits all" solution for storage and transport wasn't really feasible until recently. Generally, if you were performing a test on stool, you would be required to keep the sample frozen until processing. Depending on where you are, this may not be possible, especially if long-distance transport by road is necessary. Chemical preservation, such as with Norgen's Stool Nucleic Acid Preservation Tubes, is therefore a preferred method as it does not require cold chain transport and maintains the nucleic acid integrity of the sample for up to 2 years. It also eliminates the majority of odor, because no one wants to be the one who makes the whole lab unbearable.
The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)

When you eat something that contains non-digestible carbohydrates (NDC), it can undergo a process called fermentation, which is when microbes break down and reconfigure the NDC into different compounds. You're most likely familiar with fermentation as the process that is responsible for the production of alcohol and other compounds present in beverages such as beer and wine. In this case, instead of producing alcohol, the non-digestible carbohydrates become short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). While not the drink of choice on a Friday night, SCFAs provide insight into your metabolism as they are the main method of tracking ingested carbon as it passes through the gastrointestinal tract.1 They also serve as regulators and indicators of the state of many bodily functions, such as glucose and lipid metabolism, immunity, and appetite, therefore making an ideal target for studies on a wide range of topics.
Want to hear more from Norgen?
Join over 10,000 scientists, bioinformaticians, and researchers who receive our exclusive deals, industry updates, and more, directly to their inbox.
For a limited time, subscribe and SAVE 10% on your next purchase!
SIGN UP
In fact, SCFAs have been making a breakthrough as prospective remedy options for colorectal cancer (CRC). CRC cells have shown sensitivity to alterations of intestinal SCFA levels insinuating they have a prominent part in cell homeostasis. From inducing apoptosis in CRC cells to contributing to mitochondrial degradation, SCFAs have demonstrated promising potential for CRC management.
The Correlation Between SCFAs and Obesity
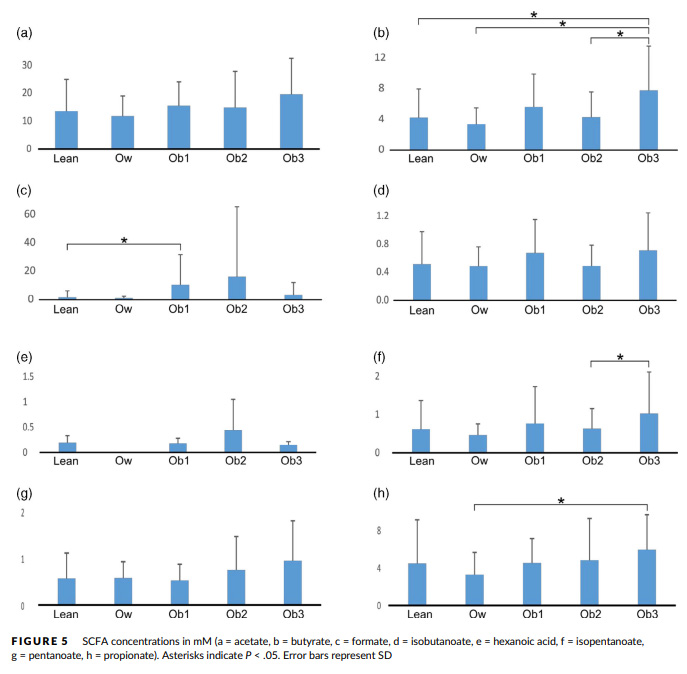
Due to easy access to high fat/high sugar foods, obesity is at epidemic levels in the US2, leading to increased strain on an already taxed healthcare system. While diet and exercise may be the only "silver bullet" when it comes to healthy weight loss, further analysis of obesity is important for discovering alternative ways to maintain a healthy weight. This is why in 2019, Gyarmati et al.3 set out to study the SCFA levels in children 5 to 12 years of age ranging from lean to obese. By analyzing stool samples stored in Norgen's Stool Nucleic Acid Preservation Tubes, the team hoped to shed more light on the pathogenesis of obesity. Previously, a linear correlation between fecal SCFA content and the degree of obesity had been reported. Of particular interest were three main compounds, propionate, acetate and butyrate. These three compounds play important roles in obesity, with propionate acting as a precursor for the formation of fat (lipogenesis), acetate being one of the originating substrates for cholesterol synthesis and butyrate supplying energy to epithelial cells.4
Future Implications of Weight Management
As expected, in the 2019 Gyarmati et al.3 study, when weight increased so too did total fecal SCFA content. The three compounds of interest were significantly elevated in the subjects who were considered obese in comparison to those with a lean body type (Figure 1). Theoretically, if these pathways could be reduced, obesity could be combatted outside of diet and exercise.
With the expansion of studies beyond the use of fecal nucleic acids, Norgen Biotek's Stool Nucleic Acid Collection and Preservation Tubes make it easy to collect and store fecal samples to be used for metatranscriptomics, metagenomics and metabolomic studies. If you work with stool samples, experience peace of mind while we facilitate a reliable, user-friendly, and reputable mode of sample preservation.